
Restaking Recap
Restaking represents an evolution in blockchain security, allowing new services and networks to leverage the cryptoeconomic security and decentralization of established blockchains like Solana and Ethereum. Unlike traditional blockchain security models, restaking enables multiple networks to benefit from the same staked assets simultaneously.
Restaking is particularly significant for new Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchains because it addresses a fundamental bootstrapping challenge. Traditionally, new networks must offer high rewards to attract stakers, as holders face significant volatility and risk with new tokens. However, established assets like BTC and ETH, being less volatile, can provide the same security with lower required rewards, making the economics more sustainable.
This benefits multiple parties in the ecosystem:
- Applications can rent security without building their own validator sets
- Stakers can earn additional rewards on their existing positions
- Networks can reduce their reliance on high inflation rates for security
However, restaking also comes with increased risks, particularly in the form of slashing. Slashing is a mechanism used in PoS blockchains to penalize validators who fail to act in the best interest of the network. In the context of restaking, the risk of slashing is increased due to the additional commitments made by the staker. For a more detailed introduction on restaking and the need for shared security, please see InfStones’ recent article on Symbiotic here.
What is Bitcoin Staking and Babylon?
While Bitcoin remains the most valuable cryptocurrency with a market cap nearing $2 trillion at the time of writing, most of this capital sits idle, unable to participate in securing other networks or generating rewards. Babylon introduces a novel solution: the Bitcoin Staking Protocol, which allows Bitcoin holders to stake and restake their BTC to secure different Proof-of-Stake based blockchains without moving their assets off the Bitcoin network.
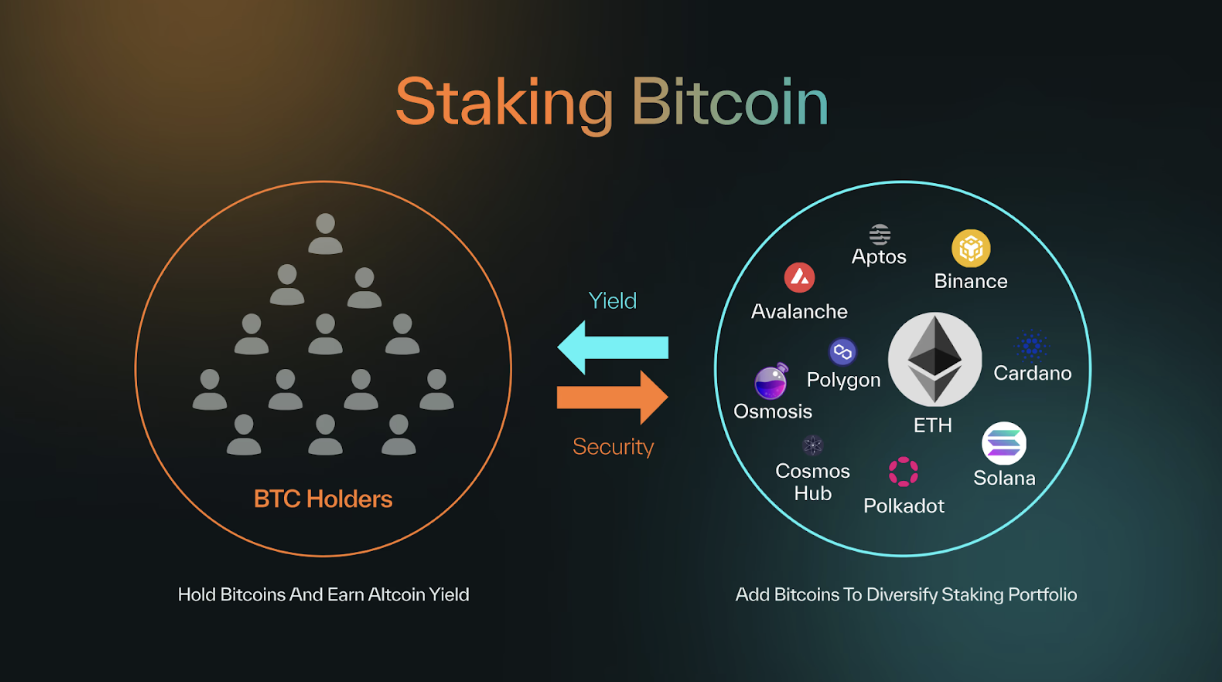
Source: Babylon
The protocol achieves this shared security model through three key components:
- A Bitcoin staking script that enables self-custodial locking of BTC
- The Babylon Chain, a Cosmos SDK-based blockchain serving as a coordination hub
- Consumer chains (IBC-enabled PoS networks) that leverage Bitcoin's security
Unlike traditional approaches that require users to wrap their Bitcoin or trust third-party custodians, Babylon's Bitcoin staking protocol is entirely self-custodial and trustless. The protocol maintains two critical properties of PoS networks:
- The ability to detect and penalize malicious actors through slashing
- Permissionless withdrawal capabilities for stakers
What makes Babylon's approach unique is that it achieves these features without requiring Bitcoin to have smart contract capabilities. When Bitcoin holders stake through Babylon, their BTC becomes stakeable collateral that can secure multiple PoS systems simultaneously, all while remaining on the Bitcoin blockchain. This allows Bitcoin holders to earn rewards while maintaining their long-term holding strategy and provides essential security infrastructure for emerging PoS networks.
The system introduces flexible delegation options where Bitcoin holders can delegate their voting power to finality providers, the Babylon network’s term for validators, without ever transferring custody of their Bitcoin. This allows even non-technical users to participate in securing PoS networks to receive additional rewards, while maintaining complete control over their assets. Most importantly, users can initiate unbonding of their staked Bitcoin at any time without requiring permission from any third party, ensuring they maintain sovereignty over their funds.
Use Cases
Babylon's architecture opens up a wide range of possibilities for both existing and new blockchain networks. Existing networks, particularly within the Cosmos ecosystem, can leverage Bitcoin's massive economic security without adding complexity to their validator operations. For new blockchain projects, Babylon provides a revolutionary solution to the bootstrap problem - allowing them to launch with strong security backing from day one while maintaining the flexibility to transition to their own security model over time.
Perhaps most excitingly, Babylon creates a foundation for expanding Bitcoin's capabilities through cryptoeconomic security. While Bitcoin's mainnet currently lacks advanced cryptographic verification features, Babylon's approach provides a pragmatic middle ground for experimentation and innovation. This enables the development of crucial infrastructure like data availability layers, shared sequencing services, and settlement layers for future Bitcoin rollups, all while maintaining lower latency than Bitcoin's native 10-minute block times.
However, it's worth noting that these use cases must be carefully designed to prevent potential attacks where malicious actors might try to manipulate the system by unbonding their stake while retaining voting power on PoS networks - a challenge that Babylon addresses through its sophisticated PoS chain architecture.
How the Babylon Protocol Works
Babylon achieves its shared security model through three key components working together: a Bitcoin staking script that enables self-custodial locking of BTC, the Babylon Chain serving as a coordination hub, and consumer chains (PoS networks) that leverage Bitcoin's security. Each component plays a vital role in enabling Bitcoin holders to secure PoS networks while maintaining complete custody of their assets.
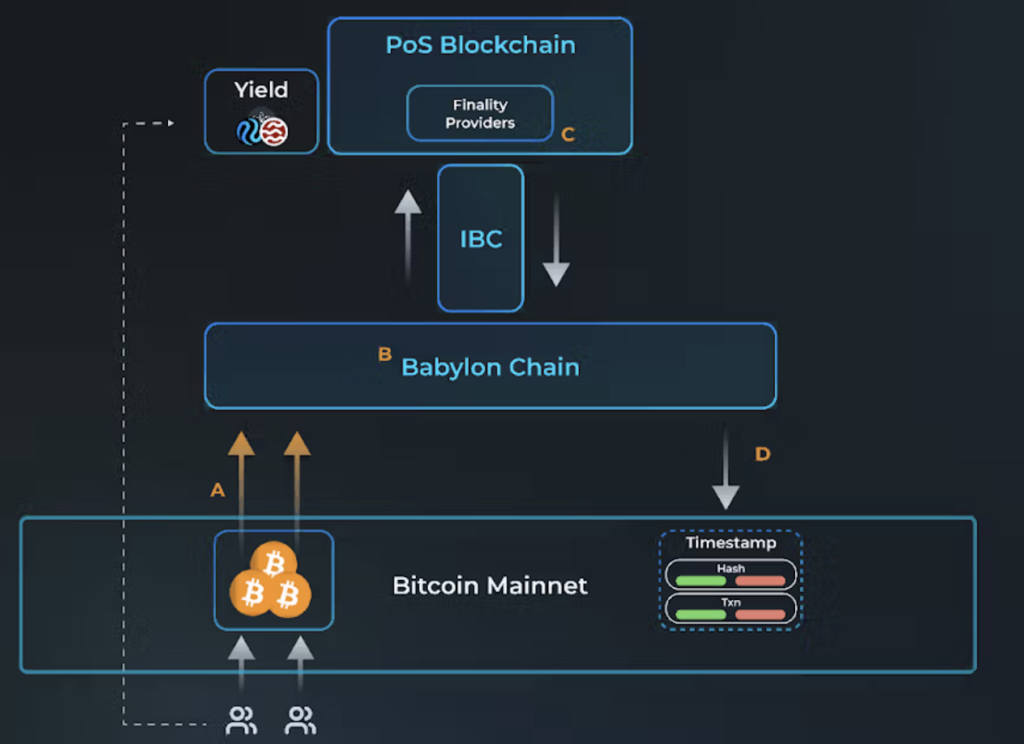
Source: Messari
Staking Mechanism and Security
Babylon's protocol utilizes Bitcoin's native UTXO model and Script capabilities to create self-custodial vaults for stakers. When Bitcoin holders stake through Babylon, they create a special transaction that locks their BTC in a vault with three predefined spending conditions. The primary condition allows withdrawal after the standard staking period. An early unbonding option enables withdrawals before this period expires, though it requires a waiting period to ensure network security. The third condition enables slashing - the burning of a portion of staked Bitcoin if malicious behavior is detected. Slashing can occur at any point, even if the Finality Provider misbehaves during the unbonding period.
To maintain protocol integrity without requiring complex smart contract capabilities, Babylon implements a covenant committee - a multi-signature group that enforces staking rules. This committee monitors and co-signs staking transactions to ensure compliance with protocol parameters, such as the fixed 33.33% slashing penalty and minimum unbonding periods. Lastly, the covenant committee ensures that slashed bitcoins are transferred to a protocol-specific address.
While the committee plays a crucial role in protocol security, its authority is strictly limited to verifying and approving transactions - it cannot access or control staked Bitcoin. The committee includes representatives from major stakeholders and can be re-elected through governance, providing additional security against potential collusion.
Babylon's security is enforced through Extractable One-Time Signatures (EOTS), a cryptographic mechanism built on Bitcoin's Schnorr signature scheme. EOTS creates a trustless slashing system where any attempt at double-signing automatically exposes the validator's private key. This exposure enables anyone on the network to execute the slashing transaction, burning the predefined 33.33% portion of staked Bitcoin. By implementing slashing directly on the Bitcoin network, Babylon creates a robust security model that doesn't rely on external oracles or complex smart contracts.
Babylon’s on-chain unbonding script requires 1008 Bitcoin blocks (approximately 7 days) to process, after which the staked collateral will expire and become available for withdrawal.
Finality Providers and Validation
Finality Providers, including InfStones, form the backbone of Babylon's consensus mechanism by operating as network validators. These providers receive delegations of staked Bitcoin and participate in an additional consensus layer beyond the base protocol. The consensus process begins with standard block validation, followed by a finality round where providers use EOTS to sign transactions. This dual-layer approach ensures both transaction validity and finality, with blocks requiring signatures from providers representing over two-thirds of staked Bitcoin before being considered final.
The validation process employs Byzantine Fault Tolerance to ensure network consensus even if some validators behave maliciously. When providers propose or validate blocks, they must sign with their EOTS keys, creating an immutable record of their actions. If a provider attempts to sign conflicting blocks at the same height - known as equivocation - their signing key is automatically exposed. This exposure triggers the slashing mechanism, burning 33.33% of all Bitcoin delegated to that provider, creating a strong economic incentive for honest behavior.
Timestamping and Cross-Chain Security
Babylon's timestamping mechanism serves as the fundamental bridge between Bitcoin's security and PoS networks. The system records cryptographic proofs of PoS chain states directly onto Bitcoin's blockchain, creating an immutable record of network history. This process involves aggregating state data from multiple consumer chains into compact checkpoints, which are then anchored to Bitcoin blocks.
The timestamping system provides crucial security benefits. For example, it prevents long-range attacks where malicious actors might try to create alternative blockchain histories after unbonding their stake - the Bitcoin timestamps provide an absolute ordering of events that cannot be altered without also modifying Bitcoin's blockchain. Additionally, the system prevents "nothing at stake" attacks by ensuring validators cannot manipulate consensus with outdated stake information, as the current validator set is always verifiable through Bitcoin's timestamps.
The Babylon PoS Chain
The Babylon Chain serves as both a standalone Proof of Stake blockchain and the synchronization system between the blockchains renting security and the staked Bitcoin. Built using the Cosmos SDK, it acts as a sophisticated coordination hub that bridges the gap between Bitcoin and PoS networks. As the first consumer of BTC security from the protocol, it demonstrates the practical implementation of Babylon's security model while managing the complex web of interactions between stakers, finality providers, and consumer chains.
A key feature of the Babylon Chain is its timestamping mechanism. When consumer chains need to record data on Bitcoin, they first send their block hashes and staking information to the Babylon Chain. Rather than each consumer chain posting directly to Bitcoin - which would be costly and inefficient - the Babylon Chain aggregates this data from multiple sources and posts it as a single checkpoint to Bitcoin. This timestamp serves as an immutable record of events, verified by Bitcoin's Proof-of-Work consensus, using block height as the measure of time rather than traditional units.
This timestamping system provides two crucial benefits to the ecosystem. First, it prevents "nothing at stake" attacks by ensuring that validators can't manipulate the system by unbonding their stake and then attempting to influence consensus with outdated information. Second, it dramatically reduces the unbonding period typically required in PoS networks. Traditional PoS systems require lengthy unbonding periods (often weeks) to protect against long-range attacks where malicious actors might try to rewrite blockchain history. By anchoring security to Bitcoin's computationally expensive Proof-of-Work chain, Babylon can safely reduce this period to hours while maintaining robust security guarantees.

Source: Babylon
How Babylon Differs from Other Shared Security Solutions
While shared security protocols like EigenLayer, Symbiotic, and Jito have gained significant traction in the Ethereum and Solana ecosystems respectively, Babylon takes a fundamentally different approach based on the following key factors:
Distinct Security Model
Unlike other shared security solutions that focus on securing specific services built on top of their native networks (like bridges, oracles, and sequencers), Babylon aims to secure entire Proof of Stake blockchains. This represents a significant expansion in scope - while Jito focuses on Solana's ecosystem services (called Node Consensus Networks) and EigenLayer & Symbiotic targets Ethereum-based services (called Actively Validated Services and Networks respectively), Babylon can theoretically secure any PoS blockchain, from Solana to Ethereum to Cosmos chains.
Native Asset Utilization
A key differentiator of Babylon is its direct approach to utilizing Bitcoin collateral exclusively, setting it apart from other major restaking protocols that rely heavily on liquid staking derivatives. While EigenLayer technically accepts native ETH deposits, almost 30% of its collateral consists of Lido's stETH and other liquid staking receipt tokens. Similarly, Symbiotic primarily accepts ETH deposits in the form of stETH, and Jito's restaking protocol on Solana primarily accepts jitoSOL - their liquid staking receipt token.
In contrast, Babylon allows Bitcoin holders to stake their BTC directly through self-custodial vaults on the Bitcoin blockchain, without any wrapping or bridging required. The process is elegantly simple: users lock their native Bitcoin in a staking contract that only they control with their private key.
Symbiotic Collateral Breakdown
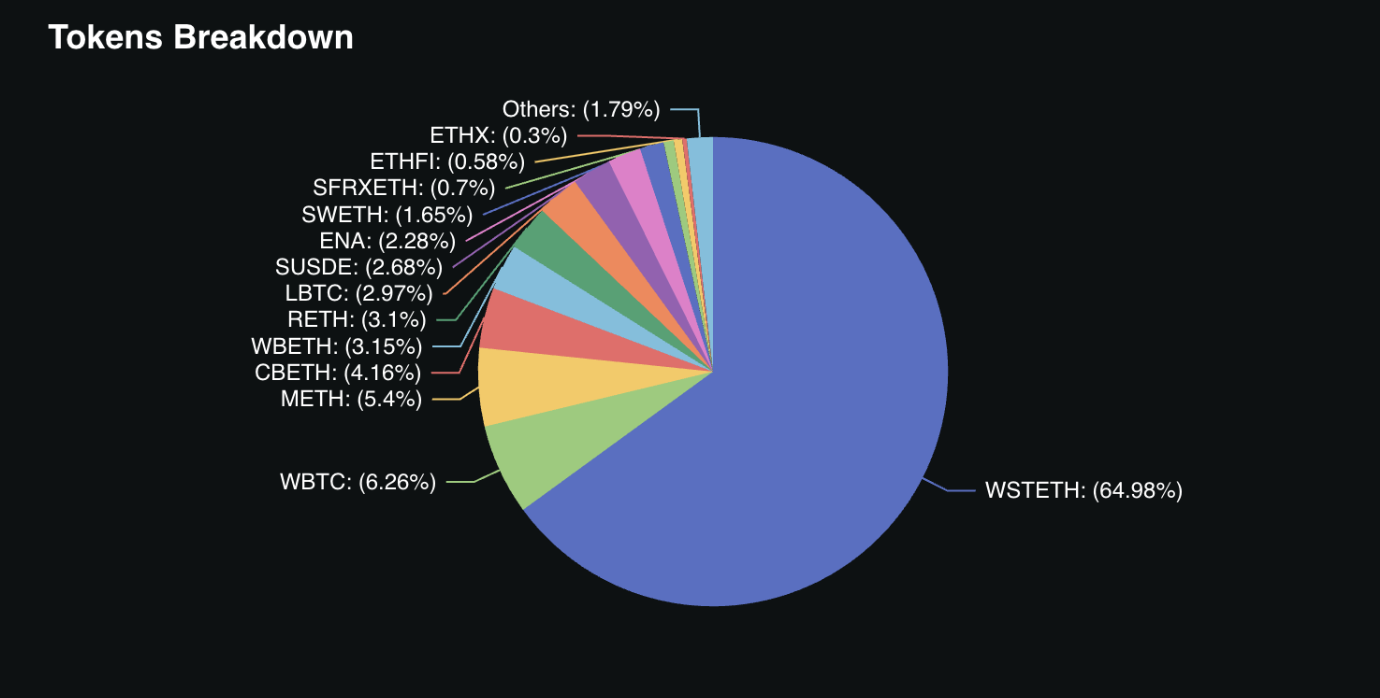
Source: DeFiLlama
Network-Native Reward Structure
Babylon introduces a unique reward model where stakers receive rewards in the native token of the network they're securing. For example, when securing the Ethereum network, Babylon BTC stakers would receive ETH rewards. This creates direct alignment between security providers and the networks they secure, unlike other staking protocols like EigenLayer where rewards are typically paid out in the network’s native gas token, ETH.
Roadmap
The Babylon mainnet launched on August 22nd, and will expand in three phases. Babylon is currently in Phase One. This phase is focused on ensuring the staking contract is fully functional.
Phase Two will activate BTC Staking with the launch of Babylon’s PoS Chain. Finality providers who received sufficient delegations in Phase One will be able to participate in the network’s consensus at this point. In addition, the Bitcoin timestamping protocol will be implemented for cross-chain time synchronization. Lastly, Phase Three will enable stakers to secure multiple PoS blockchains and earn rewards.
Following Phase One's successful launch in August, Babylon completed two significant staking cap increases. The initial Cap-1 round on August 22, 2024, filled its 1,000 BTC limit within 74 minutes, with participation from over 12,740 unique staker addresses. The more recent Cap-2 round on October 8, 2024, marked a substantial expansion, bringing total deposits to approximately 23,000 BTC (about $1.5 billion) over the course of 10 Bitcoin blocks. As of November 2024, Babylon has reached over 23,813 BTC in confirmed TVL with 33,350 delegations from 25,310 unique stakers. This dramatic increase in staked assets positions Babylon as a leading Bitcoin DeFi project, surpassing the Lightning Network's $500 million in collateral, though still below major Ethereum-based platforms like Lido ($34 billion) and EigenLayer ($14.5 billion).
During Phase One's initial rollout, Babylon implemented a points-based reward system to measure staker activity. In Cap-1 (August 2024), the protocol allocated 3,125 Babylon points per Bitcoin block, distributed proportionally among active stakes. Cap-2 (October 2024) saw significant changes to the points system, increasing the allocation to 10,000 points per Bitcoin block while maintaining the proportional distribution mechanism. While points systems have historically been used by crypto protocols as precursors to token airdrops, Babylon has not made any announcements regarding the future utility of these points.
InfStones’ Partnership with Babylon
InfStones is dedicated to supporting innovation in staking services, and we’re excited to announce our plans to accept client delegations for Babylon’s upcoming Cap-3. InfStones has been a proud partner of Babylon, running a Finality Provider for some time now, and we’re thrilled with the results! Our ongoing collaboration will help secure additional Proof of Stake blockchains while unlocking enhanced reward options for our users.
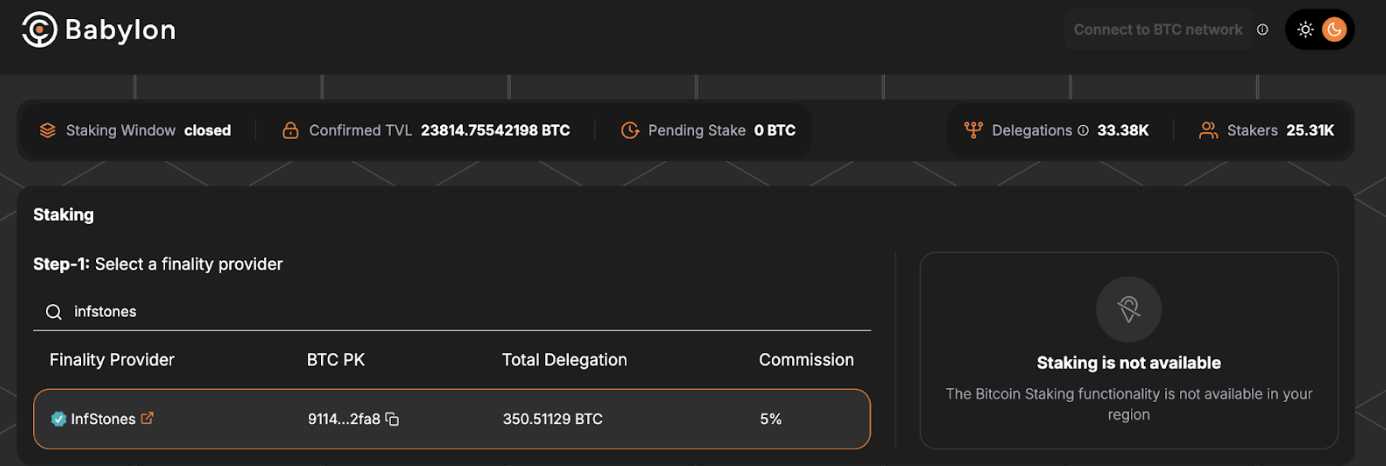
Source: Babylon
The upcoming Cap-3 phase of Babylon's Bitcoin staking protocol marks another exciting milestone in Babylon’s aim to maximize Bitcoin utility. Set to launch on December 10, 2024 at 11AM UTC, Cap-3 introduces significant expansions to the protocol's capacity and accessibility. The cap will run for approximately one week (1,000 BTC blocks) with increased transaction limits - allowing stakes between 0.005 BTC and 5,000 BTC per transaction. The points system has also been enhanced, allocating 100,000 points per block for the first 300 BTC blocks, followed by 21,000 points per block for the remaining 700 blocks and beyond, while maintaining the 0.00032 BTC unbonding transaction fee.
While Bitcoin staking might seem like a novel concept, Babylon has made it as intuitive as traditional Proof of Stake delegation, all while maintaining Bitcoin's fundamental principles of security and self-custody. What makes Babylon particularly exciting is how far we've come in such a short time. Just a few years ago, the idea of staking Bitcoin seemed impossible - Bitcoin was viewed solely as digital gold, destined to remain idle in wallets. Now, our clients can put their Bitcoin to work securing multiple Proof of Stake networks while earning additional rewards through InfStones' industry-leading staking infrastructure. Contact our team today to learn how you can participate in the evolution of Bitcoin staking with Babylon.
Article written by Rohit Sarkar, Business Operation Generalist at InfStones.
InfStones is an advanced, enterprise-grade Platform as a Service (PaaS) blockchain infrastructure provider trusted by the top blockchain companies in the world. InfStones’ AI-based infrastructure provides developers worldwide with a rugged, powerful node management platform alongside an easy-to-use API. With over 20,000 nodes supported on over 80 blockchains, InfStones gives developers all the control they need - reliability, speed, efficiency, security, and scalability - for cross-chain DeFi, NFT, GameFi, and decentralized application development.
InfStones is trusted by the biggest blockchain companies in the world including Binance, CoinList, BitGo, OKX, Chainlink, Polygon, Harmony, and KuCoin, among a hundred other customers. InfStones is dedicated to developing the next evolution of a better world through limitless Web3 innovation.